[cs_content][cs_element_section _id="1"][cs_element_row _id="2"][cs_element_column _id="3"][cs_text _order="0"]
2018 began with a landmark study led by Gregory Albers, MD, Stanford School of Medicine showing that acute strokes can be treated hours longer after symptoms appear than previously thought. The DEFUSE 3 trial (Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging Evaluation for Understanding Stroke Evaluation) published in The New England Journal of Medicine shows strokes can be treated up to 16 hours after symptoms begin with significant improvement. Key to the treatment approach was the use of advanced imaging technology to assess the ratio of ischemic tissue to infarct volume after acute stroke. Based on the imaging findings, physicians used endovascular thrombectomy on patients with infarct size of <70mL and ischemic tissue:infarct volume ≥1.8. 45% of patient who were treated with endovascular thrombectomy and standard medical therapy were functionally independent compared to only 17% treated with standard medical therapy.
[/cs_text][x_custom_headline level="h2" looks_like="h3" accent="false"]Can Doctors Use The New Approach When Treating Acute Stroke in the Elderly?[/x_custom_headline][cs_text]
The new American Heart Association/American Stroke Association 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients provides guidance to healthcare professionals about extending the acute stroke treatment window from 6 hours to 24 hours after symptoms appear, when the appropriate patient population is treated. The AHA/ASA recommended a change in practice based on findings from the DAWN trial (Clinical Mismatch in the Triage of Wake Up and Late Presenting Stroke Undergoing Neurointervention with Trevo) and the DEFUSE 3 trial. The changes increase the number of stroke patients who can now be treated with lifesaving technologies like clot-dissolving agents and mechanical thrombectomy with stent retrievers.
[/cs_text][x_custom_headline level="h2" looks_like="h3" accent="false"]How Long Can A Stroke Be Treated After Symptoms Appear?[/x_custom_headline][cs_text]
As many as 20% of individuals with an acute stroke can now be treated up to 24 hours after symptoms. Strokes occur when people sleep so they do not have the exact time of the event. Also symptoms are not obvious to a person immediately, but is obvious to a person looking at them. The updated guidelines enable physicians to treat certain cases of acute stroke for a longer period of time so know the signs of acute stroke and take action to save someone's life.
[/cs_text][x_custom_headline level="h2" looks_like="h3" accent="false"]Do You Know The Signs of A Stroke?[/x_custom_headline][cs_text]
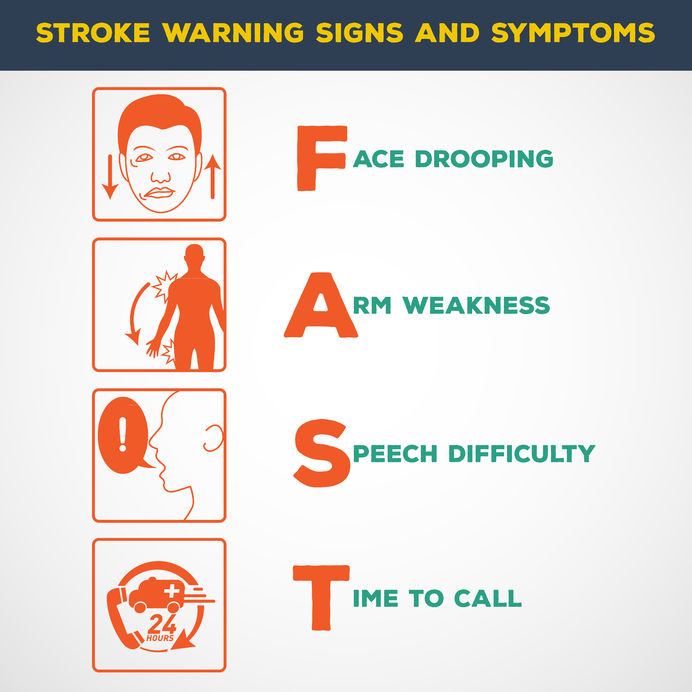
The American Stroke Association uses the letters in FAST to remember and note the signs of a stroke. Face Drooping, Arm Weakness, Speech Difficulty,Time to Call 911. Other signs of stroke are numbness or weakness especially on one side of the body, confusion, trouble speaking, trouble seeing, trouble walking, severe headache with no known cause.
What Should I Do If I Or Someone I Know Has A Stroke? Remember FAST ? Time to Call 911. ---- Julie Ellison, PhD
[/cs_text][/cs_element_column][/cs_element_row][/cs_element_section][/cs_content]